Securing AWS EKS with Okta OIDC: Deep Technical Implementation
— eks, aws, kubernetes, okta, oidc, security, authentication — 18 min read
Your organization runs multiple EKS clusters. Engineers share IAM credentials. Audit logs show generic service accounts. When someone leaves, you manually revoke access across 20+ clusters. This isn't sustainable.
We solved this by implementing Okta OIDC authentication for AWS EKS. This guide provides the complete technical implementation, from protocol mechanics to production deployment.
Deep Dive: OIDC Protocol Mechanics
What is OpenID Connect?
OIDC is an authentication layer built on OAuth 2.0. It adds:
- Identity verification through ID tokens (JWT format)
- Standard claims for user information
- Discovery mechanism for configuration
- Dynamic client registration
- Session management
The Three-Token Architecture
OIDC uses three distinct tokens:
1. ID Token (JWT): Purpose: Proves user identity Format: Signed JWT Contains: User claims, groups, email Lifetime: Short (5-60 minutes) 2. Access Token: Purpose: Authorizes API access Format: Opaque or JWT Contains: Scopes, audience Lifetime: Short (5-60 minutes) 3. Refresh Token: Purpose: Obtain new tokens Format: Opaque string Contains: Reference to session Lifetime: Long (hours to days)OIDC Discovery Mechanism
Every OIDC provider exposes a discovery endpoint:
curl https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default/.well-known/openid-configurationReturns critical configuration:
{ "issuer": "https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default", "authorization_endpoint": "https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default/v1/authorize", "token_endpoint": "https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default/v1/token", "userinfo_endpoint": "https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default/v1/userinfo", "jwks_uri": "https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default/v1/keys", "response_types_supported": ["code", "token", "id_token"], "subject_types_supported": ["public"], "id_token_signing_alg_values_supported": ["RS256"], "scopes_supported": ["openid", "profile", "email", "groups"], "token_endpoint_auth_methods_supported": ["client_secret_basic", "client_secret_post"], "claims_supported": ["iss", "sub", "aud", "iat", "exp", "email", "groups"]}Deep Dive: Authentication Flow
Complete Authorization Code Flow
Here's exactly what happens when you run kubectl get pods:
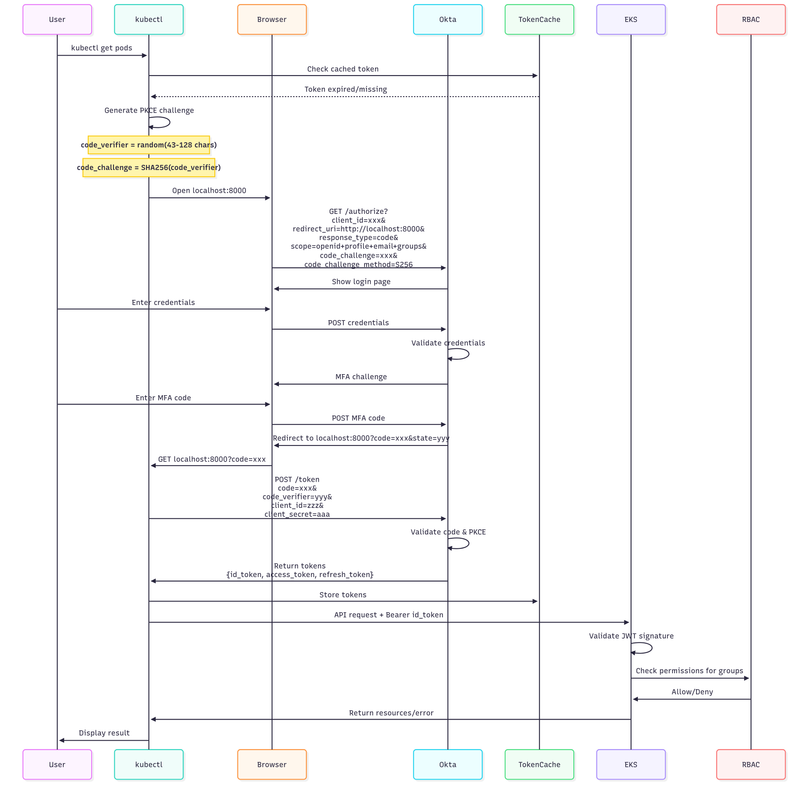
PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange)
PKCE prevents authorization code interception:
# Step 1: Generate code verifier (kubectl)import secretsimport hashlibimport base64
code_verifier = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(secrets.token_bytes(32)).decode('utf-8').rstrip('=')# Example: "dBjftJeZ4CVP-mB92K27uhbUJU1p1r_wW1gFWFOEjXk"
# Step 2: Generate code challengecode_challenge = base64.urlsafe_b64encode( hashlib.sha256(code_verifier.encode()).digest()).decode('utf-8').rstrip('=')# Example: "E9Melhoa2OwvFrEMTJguCHaoeK1t8URWbuGJSstw-cM"
# Step 3: Include in authorization requestauth_url = f"""https://okta.com/oauth2/default/v1/authorize? client_id={client_id}& redirect_uri=http://localhost:8000& response_type=code& scope=openid+profile+email+groups& code_challenge={code_challenge}& code_challenge_method=S256& state={state}"""
# Step 4: Exchange code with verifiertoken_request = { "grant_type": "authorization_code", "code": authorization_code, "redirect_uri": "http://localhost:8000", "client_id": client_id, "client_secret": client_secret, "code_verifier": code_verifier # Proves we initiated the request}Deep Dive: JWT Structure and Validation
Anatomy of the ID Token
The ID token has three parts separated by dots:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IlcuLi4ifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL2NvbXBhbnkub2t0YS5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiIwMHUxYmNkZTJmZ2hpSktMTU4zIiwiZW1haWwiOiJzYXJhaEBjb21wYW55LmNvbSIsImdyb3VwcyI6WyJhd3MtZWtzLWRldmVsb3BlcnMiXX0.X5K_zK3N...Decoded:
// HEADER{ "alg": "RS256", // RSA signature with SHA-256 "kid": "W4F8YHJ3K9XFS5T", // Key ID for signature verification "typ": "JWT", // Token type "x5t": "fb011aeb7b1c3e..." // X.509 certificate thumbprint}
// PAYLOAD{ // Registered Claims (RFC 7519) "iss": "https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default", // Issuer "sub": "00u1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4", // Subject (user ID) "aud": "0oa1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4", // Audience (client ID) "exp": 1704315600, // Expiration (Unix timestamp) "iat": 1704312000, // Issued at "auth_time": 1704311940, // Authentication time "nonce": "n-0S6_WzA2Mj", // Replay attack prevention // Standard OIDC Claims "email": "sarah.chen@company.com", "email_verified": true, "name": "Sarah Chen", "preferred_username": "sarah.chen", "given_name": "Sarah", "family_name": "Chen", "locale": "en-US", "zoneinfo": "America/Los_Angeles", // Custom Claims (Critical for RBAC) "groups": [ "aws-eks-developers", "aws-eks-team-platform", "aws-eks-oncall" ], // Authentication Context "amr": ["pwd", "mfa", "otp"], // Authentication methods used "acr": "urn:okta:loa:2fa", // Authentication context reference "idp": "00o1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4" // Identity provider reference}
// SIGNATURE"X5K_zK3N3jkSBqGATTLSe5okM3U7WULhGqWbUll8c4p..."JWT Signature Verification Process
EKS performs these exact steps:
// Step 1: Fetch JWKS (JSON Web Key Set)func fetchJWKS(issuerURL string) (*jose.JSONWebKeySet, error) { jwksURL := issuerURL + "/.well-known/jwks.json" resp, err := http.Get(jwksURL) if err != nil { return nil, err } defer resp.Body.Close() var jwks jose.JSONWebKeySet if err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&jwks); err != nil { return nil, err } return &jwks, nil}
// Step 2: Verify token signaturefunc verifyToken(tokenString string, jwks *jose.JSONWebKeySet) (*jwt.Claims, error) { // Parse token without verification first token, err := jwt.ParseSigned(tokenString) if err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("malformed token: %w", err) } // Get key ID from token header kid := token.Headers[0].KeyID // Find matching key in JWKS keys := jwks.Key(kid) if len(keys) == 0 { return nil, fmt.Errorf("key %s not found", kid) } // Verify signature and extract claims var claims jwt.Claims var customClaims map[string]interface{} if err := token.Claims(keys[0], &claims, &customClaims); err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to verify signature: %w", err) } // Step 3: Validate standard claims expected := jwt.Expected{ Issuer: "https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default", Audience: jwt.Audience{"0oa1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4"}, Time: time.Now(), } if err := claims.Validate(expected); err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid claims: %w", err) } return &claims, nil}JWKS (JSON Web Key Set) Structure
Okta's JWKS endpoint returns:
{ "keys": [ { "kty": "RSA", "alg": "RS256", "kid": "W4F8YHJ3K9XFS5T", "use": "sig", "e": "AQAB", "n": "0WHMhwpG4Y3aLpuMOKpnQX...", // RSA modulus (base64) "x5c": [ "MIIDqDCCApCgAwIBAgIGAV..." // X.509 certificate chain ], "x5t": "fb011aeb7b1c3e48e3ff..." // Certificate thumbprint } ]}Deep Dive: EKS API Server Authentication
Kubernetes Authentication Architecture
┌─────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐│ kubectl │────▶│ EKS API Server │────▶│ Authentication │└─────────────┘ └──────────────────┘ │ Plugins │ │ └─────────────────┘ │ │ ▼ ▼ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ │ Authorization │ │ OIDC Verifier │ │ (RBAC/ABAC) │ │ (Okta JWT) │ └──────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ │ ▼ ┌──────────────────┐ │ Admission │ │ Controllers │ └──────────────────┘API Server OIDC Configuration
When you configure OIDC, EKS adds these flags to the API server:
kube-apiserver: # OIDC Configuration --oidc-issuer-url=https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default --oidc-client-id=0oa1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4 --oidc-username-claim=email --oidc-username-prefix=okta: --oidc-groups-claim=groups --oidc-groups-prefix=okta: --oidc-required-claim=aud=0oa1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4 # Token validation --oidc-signing-algs=RS256 --oidc-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/oidc-ca.crt # Authentication flow --authentication-token-webhook-cache-ttl=10m --authentication-token-webhook-version=v1Authentication Request Flow in API Server
// Simplified API server authentication flowfunc (s *APIServer) authenticateRequest(req *http.Request) (*user.Info, error) { // 1. Extract bearer token token := extractBearerToken(req) if token == "" { return nil, errors.New("no bearer token") } // 2. Check token cache if cachedUser, found := s.tokenCache.Get(token); found { return cachedUser, nil } // 3. Verify OIDC token userInfo, err := s.oidcAuthenticator.AuthenticateToken(token) if err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("OIDC authentication failed: %w", err) } // 4. Cache successful authentication s.tokenCache.Set(token, userInfo, 10*time.Minute) // 5. Audit log audit.LogAuthentication(userInfo, req) return userInfo, nil}
// OIDC Authenticator implementationtype OIDCAuthenticator struct { issuerURL string clientID string usernameClaim string groupsClaim string usernamePrefix string groupsPrefix string verifier *oidc.IDTokenVerifier}
func (o *OIDCAuthenticator) AuthenticateToken(token string) (*user.Info, error) { // 1. Verify token idToken, err := o.verifier.Verify(context.Background(), token) if err != nil { return nil, err } // 2. Extract claims var claims map[string]interface{} if err := idToken.Claims(&claims); err != nil { return nil, err } // 3. Build user info userInfo := &user.Info{ Username: o.usernamePrefix + claims[o.usernameClaim].(string), UID: claims["sub"].(string), Extra: make(map[string][]string), } // 4. Extract groups if groups, ok := claims[o.groupsClaim].([]interface{}); ok { for _, group := range groups { userInfo.Groups = append(userInfo.Groups, o.groupsPrefix + group.(string)) } } return userInfo, nil}Deep Dive: RBAC Evaluation Engine
How Kubernetes RBAC Works
RBAC uses four key objects:
1. Role/ClusterRole: Defines permissions2. RoleBinding/ClusterRoleBinding: Grants permissions3. Subject: User, Group, or ServiceAccount4. Verb: Action (get, list, create, update, delete, watch)RBAC Evaluation Algorithm
// Simplified RBAC authorizationfunc (r *RBACAuthorizer) Authorize(attrs authorization.Attributes) (bool, string, error) { // 1. Get user info from request user := attrs.GetUser() // 2. Check cluster-wide permissions if r.authorizeClusterScope(user, attrs) { return true, "ClusterRoleBinding match", nil } // 3. Check namespace permissions if attrs.GetNamespace() != "" { if r.authorizeNamespaceScope(user, attrs) { return true, "RoleBinding match", nil } } // 4. No matching rules return false, "no RBAC policy matched", nil}
func (r *RBACAuthorizer) authorizeClusterScope(user user.Info, attrs authorization.Attributes) bool { // Check all ClusterRoleBindings for _, binding := range r.clusterRoleBindings { // Check if user/group matches subjects if !r.subjectMatches(user, binding.Subjects) { continue } // Get the ClusterRole role := r.getClusterRole(binding.RoleRef) if role == nil { continue } // Check if role allows the action if r.ruleAllows(role.Rules, attrs) { return true } } return false}
func (r *RBACAuthorizer) subjectMatches(user user.Info, subjects []rbac.Subject) bool { for _, subject := range subjects { switch subject.Kind { case "User": if subject.Name == user.GetName() { return true } case "Group": for _, group := range user.GetGroups() { if subject.Name == group { return true } } } } return false}
func (r *RBACAuthorizer) ruleAllows(rules []rbac.PolicyRule, attrs authorization.Attributes) bool { for _, rule := range rules { // Check API group if !r.matchesAPIGroup(rule.APIGroups, attrs.GetAPIGroup()) { continue } // Check resource if !r.matchesResource(rule.Resources, attrs.GetResource()) { continue } // Check verb if !r.matchesVerb(rule.Verbs, attrs.GetVerb()) { continue } // Check resource name if specified if len(rule.ResourceNames) > 0 { if !r.matchesResourceName(rule.ResourceNames, attrs.GetName()) { continue } } return true } return false}RBAC Rules Evaluation Example
When okta:sarah@company.com in group okta:aws-eks-developers runs:
kubectl get pods -n team-platformThe evaluation process:
Request Attributes: User: okta:sarah@company.com Groups: [okta:aws-eks-developers, okta:aws-eks-team-platform] Verb: get Resource: pods Namespace: team-platform APIGroup: ""
Evaluation Steps:1. Check ClusterRoleBindings: - okta-developers binding found - Subject group "okta:aws-eks-developers" matches - ClusterRole "developer-role" retrieved - Rule allows: {APIGroups: [""], Resources: ["pods"], Verbs: ["get"]} ✓ ALLOWED
2. Check RoleBindings in namespace: - team-admins binding found - Subject group "okta:aws-eks-team-platform" matches - ClusterRole "admin" grants full namespace access ✓ ALLOWED (higher privilege)
Result: Authorized via ClusterRoleBindingComplete Production Implementation
Phase 1: Okta Setup with Security Hardening
Configure Application Security
// Okta Application Advanced Settings{ "application": { "label": "AWS EKS Production", "signOnMode": "OPENID_CONNECT", "settings": { "oauthClient": { "issuer_mode": "CUSTOM_URL", "consent_method": "TRUSTED", "application_type": "web", "grant_types": ["authorization_code", "refresh_token"], "response_types": ["code"], "refresh_token": { "rotation_type": "ROTATE", "leeway": 30 }, "dpop_bound_access_tokens": true } }, "credentials": { "oauthClient": { "token_endpoint_auth_method": "client_secret_jwt", "autoKeyRotation": true } } }}Advanced Group Rules
// Dynamic group membership based on attributes{ "type": "group_rule", "name": "Auto-assign developers", "conditions": { "people": { "users": { "exclude": [] } }, "expression": { "value": "user.department == \"Engineering\" AND user.employeeType == \"FTE\"", "type": "urn:okta:expression:1.0" } }, "actions": { "assignUserToGroups": { "groupIds": ["aws-eks-developers"] } }}Phase 2: EKS Configuration with High Availability
Multi-Region OIDC Setup
# eks-multi-region-oidc.yamlapiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5kind: ClusterConfig
metadata: name: production-cluster region: us-west-2 version: "1.31"
iam: withOIDC: true serviceAccounts: - metadata: name: oidc-refresh-controller namespace: kube-system attachPolicyARNs: - arn:aws:iam::123456789012:policy/OIDCRefreshPolicy
identityProviders: - name: okta-primary type: oidc issuerUrl: https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default clientId: 0oa1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4 usernameClaim: email usernamePrefix: "okta:" groupsClaim: groups groupsPrefix: "okta:" requiredClaims: aud: "0oa1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4" iss: "https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default" tags: Environment: production DisasterRecovery: enabled
- name: okta-backup type: oidc issuerUrl: https://company-dr.okta.com/oauth2/default clientId: 0oa2bcde3fghiJKLMN4o5 usernameClaim: email usernamePrefix: "okta-dr:" groupsClaim: groups groupsPrefix: "okta-dr:"RBAC with Fine-Grained Permissions
# rbac-production.yaml---# Developer role with verb restrictionsapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRolemetadata: name: developer-restrictedrules:# Read-only cluster resources- apiGroups: [""] resources: ["namespaces", "nodes", "persistentvolumes"] verbs: ["get", "list"] # Namespace-scoped resources with restrictions- apiGroups: ["apps"] resources: ["deployments", "replicasets"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"] # Cannot delete deployments - apiGroups: ["apps"] resources: ["deployments/scale"] verbs: ["update", "patch"] # Pod management with restrictions- apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "delete"] # Cannot create pods directly (must use deployments) - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods/log", "pods/status"] verbs: ["get", "list"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods/exec", "pods/portforward"] verbs: ["create"] # Requires additional admission webhook validation # ConfigMaps and Secrets - read only- apiGroups: [""] resources: ["configmaps", "secrets"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"] # Services and Ingresses- apiGroups: ["", "networking.k8s.io"] resources: ["services", "ingresses"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---# Platform team elevated permissionsapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRolemetadata: name: platform-engineerrules:- apiGroups: ["*"] resources: ["*"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"] - apiGroups: ["apps", "batch", "autoscaling"] resources: ["*"] verbs: ["*"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods/exec", "pods/portforward"] verbs: ["create"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["secrets", "configmaps"] verbs: ["create", "update", "patch", "delete"] # Deny certain critical operations- apiGroups: [""] resources: ["nodes", "persistentvolumes"] verbs: ["create", "update", "patch", "delete"] # Handled by cluster-admin only
---# Namespace admin templateapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: Rolemetadata: name: namespace-admin namespace: team-platformrules:- apiGroups: ["*"] resources: ["*"] verbs: ["*"] # Full control within namespace - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["resourcequotas", "limitranges"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"] # Cannot modify quotasPhase 3: Authentication Flow Implementation
Custom Token Refresh Controller
// token-refresh-controller/main.gopackage main
import ( "context" "encoding/json" "fmt" "net/http" "net/url" "strings" "time" "github.com/coreos/go-oidc/v3/oidc" "golang.org/x/oauth2" corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1" metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1" "k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes")
type TokenRefreshController struct { k8sClient kubernetes.Interface oidcProvider *oidc.Provider oauth2Config oauth2.Config}
func (c *TokenRefreshController) RefreshToken(ctx context.Context, refreshToken string) (*oauth2.Token, error) { // Build refresh request data := url.Values{} data.Set("grant_type", "refresh_token") data.Set("refresh_token", refreshToken) data.Set("client_id", c.oauth2Config.ClientID) data.Set("client_secret", c.oauth2Config.ClientSecret) req, err := http.NewRequestWithContext(ctx, "POST", c.oauth2Config.Endpoint.TokenURL, strings.NewReader(data.Encode())) if err != nil { return nil, err } req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded") // Execute request resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req) if err != nil { return nil, err } defer resp.Body.Close() // Parse response var token oauth2.Token if err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&token); err != nil { return nil, err } return &token, nil}
func (c *TokenRefreshController) ValidateAndRefreshSecret(ctx context.Context, secret *corev1.Secret) error { // Extract token from secret tokenData, ok := secret.Data["token"] if !ok { return fmt.Errorf("token not found in secret") } // Parse and validate token idToken, err := c.oidcProvider.Verifier(&oidc.Config{ ClientID: c.oauth2Config.ClientID, }).Verify(ctx, string(tokenData)) if err != nil { // Token invalid or expired, try refresh refreshToken, ok := secret.Data["refresh_token"] if !ok { return fmt.Errorf("refresh token not found") } newToken, err := c.RefreshToken(ctx, string(refreshToken)) if err != nil { return fmt.Errorf("token refresh failed: %w", err) } // Update secret with new token secret.Data["token"] = []byte(newToken.AccessToken) if newToken.RefreshToken != "" { secret.Data["refresh_token"] = []byte(newToken.RefreshToken) } secret.Data["expires_at"] = []byte(newToken.Expiry.Format(time.RFC3339)) _, err = c.k8sClient.CoreV1().Secrets(secret.Namespace).Update( ctx, secret, metav1.UpdateOptions{}) return err } // Token still valid return nil}
func (c *TokenRefreshController) Run(ctx context.Context) { ticker := time.NewTicker(5 * time.Minute) defer ticker.Stop() for { select { case <-ticker.C: // List all OIDC token secrets secrets, err := c.k8sClient.CoreV1().Secrets("").List(ctx, metav1.ListOptions{ LabelSelector: "type=oidc-token", }) if err != nil { fmt.Printf("Error listing secrets: %v\n", err) continue } // Validate and refresh each token for _, secret := range secrets.Items { if err := c.ValidateAndRefreshSecret(ctx, &secret); err != nil { fmt.Printf("Error refreshing token for %s/%s: %v\n", secret.Namespace, secret.Name, err) } } case <-ctx.Done(): return } }}Phase 4: Advanced Security Patterns
Zero Trust Network Access
# network-policies.yamlapiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1kind: NetworkPolicymetadata: name: deny-all-ingress namespace: productionspec: podSelector: {} policyTypes: - Ingress ---# Allow only from authenticated servicesapiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1kind: NetworkPolicymetadata: name: allow-authenticated-ingress namespace: productionspec: podSelector: matchLabels: app: api-server policyTypes: - Ingress ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: name: ingress-nginx - podSelector: matchLabels: app: oauth-proxy ports: - protocol: TCP port: 8080Admission Webhook for OIDC Validation
// admission-webhook/main.gopackage main
import ( "context" "encoding/json" "fmt" "net/http" admissionv1 "k8s.io/api/admission/v1" corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1" metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1")
type OIDCAdmissionWebhook struct { requiredGroups []string requiredClaims map[string]string}
func (w *OIDCAdmissionWebhook) Handle(req *admissionv1.AdmissionRequest) *admissionv1.AdmissionResponse { // Extract user info from request userInfo := req.UserInfo // Check if user has required groups hasRequiredGroup := false for _, requiredGroup := range w.requiredGroups { for _, userGroup := range userInfo.Groups { if userGroup == requiredGroup { hasRequiredGroup = true break } } } if !hasRequiredGroup { return &admissionv1.AdmissionResponse{ Allowed: false, Result: &metav1.Status{ Message: fmt.Sprintf("User %s lacks required groups: %v", userInfo.Username, w.requiredGroups), }, } } // Additional validation for sensitive operations if req.Kind.Kind == "Secret" && req.Operation == admissionv1.Delete { // Require platform-admin group for secret deletion hasPlatformAdmin := false for _, group := range userInfo.Groups { if group == "okta:aws-eks-platform-admin" { hasPlatformAdmin = true break } } if !hasPlatformAdmin { return &admissionv1.AdmissionResponse{ Allowed: false, Result: &metav1.Status{ Message: "Secret deletion requires platform-admin group", }, } } } // Check namespace restrictions var pod corev1.Pod if err := json.Unmarshal(req.Object.Raw, &pod); err == nil { // Validate pod security context if pod.Spec.SecurityContext != nil && pod.Spec.SecurityContext.RunAsUser != nil && *pod.Spec.SecurityContext.RunAsUser == 0 { // Running as root requires special permission hasRootPermission := false for _, group := range userInfo.Groups { if group == "okta:aws-eks-root-allowed" { hasRootPermission = true break } } if !hasRootPermission { return &admissionv1.AdmissionResponse{ Allowed: false, Result: &metav1.Status{ Message: "Running pods as root requires aws-eks-root-allowed group", }, } } } } return &admissionv1.AdmissionResponse{ Allowed: true, }}Production Operations
Monitoring and Observability
Prometheus Metrics
# prometheus-rules.yamlapiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1kind: PrometheusRulemetadata: name: oidc-authenticationspec: groups: - name: oidc.rules interval: 30s rules: - alert: HighAuthenticationFailureRate expr: | ( sum(rate(apiserver_authentication_attempts{result="error"}[5m])) / sum(rate(apiserver_authentication_attempts[5m])) ) > 0.1 for: 5m labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: High authentication failure rate detected description: "{{ $value | humanizePercentage }} of authentication attempts are failing" - alert: OIDCTokenExpirationsSpiking expr: | rate(apiserver_authentication_token_cache_fetch_total{result="expired"}[5m]) > 10 for: 5m labels: severity: info annotations: summary: High rate of token expirations description: "{{ $value }} tokens expiring per second" - alert: RBACDenialRate expr: | sum by (username) ( rate(apiserver_authorization_attempts{result="forbidden"}[5m]) ) > 1 for: 10m labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: User experiencing high RBAC denial rate description: "User {{ $labels.username }} denied {{ $value }} times per second"Audit Logging Configuration
# audit-policy.yamlapiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1kind: Policyrules: # Log all requests from OIDC users at Metadata level - level: Metadata users: ["okta:*"] stages: - ResponseComplete # Detailed logging for sensitive operations - level: RequestResponse users: ["okta:*"] verbs: ["create", "update", "patch", "delete"] resources: - group: "" resources: ["secrets", "configmaps"] - group: "rbac.authorization.k8s.io" resources: ["roles", "rolebindings", "clusterroles", "clusterrolebindings"] # Log authentication failures - level: Metadata omitStages: - RequestReceived users: ["system:anonymous"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]Disaster Recovery
Backup Identity Provider Configuration
#!/bin/bash# backup-oidc-config.sh
CLUSTER_NAME="production-cluster"BACKUP_DIR="./oidc-backups/$(date +%Y%m%d)"
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR
# Backup OIDC provider configurationaws eks describe-identity-provider-config \ --cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME \ --identity-provider-config type=oidc,name=okta \ > $BACKUP_DIR/oidc-config.json
# Backup RBAC policieskubectl get clusterroles,clusterrolebindings,roles,rolebindings \ --all-namespaces -o yaml \ > $BACKUP_DIR/rbac-policies.yaml
# Backup Okta application configurationcurl -X GET "https://company.okta.com/api/v1/apps/0oa1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4" \ -H "Authorization: SSWS ${OKTA_API_TOKEN}" \ > $BACKUP_DIR/okta-app-config.json
# Encrypt backupstar czf - $BACKUP_DIR | \ openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -salt -out $BACKUP_DIR.tar.gz.enc
echo "Backup completed: $BACKUP_DIR.tar.gz.enc"Emergency Break-Glass Access
# break-glass-access.yamlapiVersion: v1kind: ServiceAccountmetadata: name: break-glass-admin namespace: kube-system annotations: purpose: "Emergency access when OIDC is unavailable" expires: "2024-12-31T23:59:59Z"---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRoleBindingmetadata: name: break-glass-admin-binding annotations: purpose: "Emergency access binding"roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-adminsubjects:- kind: ServiceAccount name: break-glass-admin namespace: kube-system---apiVersion: v1kind: Secretmetadata: name: break-glass-token namespace: kube-system annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: break-glass-admintype: kubernetes.io/service-account-tokenPerformance Optimization
API Server Tuning
# api-server-config.yamlapiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3kind: ClusterConfigurationapiServer: extraArgs: # OIDC specific oidc-issuer-url: "https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default" oidc-client-id: "0oa1bcde2fghiJKLMN3o4" oidc-username-claim: "email" oidc-groups-claim: "groups" # Performance tuning max-requests-inflight: "1000" max-mutating-requests-inflight: "500" # Token caching authentication-token-webhook-cache-ttl: "10m" authorization-webhook-cache-authorized-ttl: "10m" authorization-webhook-cache-unauthorized-ttl: "30s" # Audit logging optimization audit-log-maxage: "30" audit-log-maxbackup: "10" audit-log-maxsize: "100" audit-log-compress: "true" # Request timeout request-timeout: "60s" # TLS configuration tls-cipher-suites: "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256" tls-min-version: "VersionTLS12"Client-Side Optimization
# kubeconfig-optimized.yamlapiVersion: v1kind: Configclusters:- cluster: certificate-authority-data: ${CA_DATA} server: https://eks-endpoint.amazonaws.com # Connection pooling tls-server-name: eks-endpoint.amazonaws.com proxy-url: "" name: production
users:- name: okta-user user: exec: apiVersion: client.authentication.k8s.io/v1beta1 command: kubectl args: - oidc-login - get-token - --oidc-issuer-url=https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default - --oidc-client-id=${CLIENT_ID} - --oidc-client-secret=${CLIENT_SECRET} # Performance optimizations - --oidc-extra-scope=offline_access - --token-cache-dir=/tmp/kubectl-oidc-cache - --skip-open-browser - --listen-address=127.0.0.1:8000 env: - name: KUBECTL_OIDC_TOKEN_CACHE_SIZE value: "1000" - name: KUBECTL_OIDC_TOKEN_CACHE_TTL value: "3600"Troubleshooting Deep Dive
Debug Token Issues
#!/bin/bash# debug-token.sh
# 1. Get raw tokenTOKEN=$(kubectl config view --raw -o jsonpath='{.users[?(@.name=="okta-user")].user.auth-provider.config.id-token}')
# 2. Decode headerecho "=== TOKEN HEADER ==="echo $TOKEN | cut -d. -f1 | base64 -d 2>/dev/null | jq .
# 3. Decode payloadecho "=== TOKEN PAYLOAD ==="echo $TOKEN | cut -d. -f2 | base64 -d 2>/dev/null | jq .
# 4. Verify signatureecho "=== SIGNATURE VERIFICATION ==="curl -s https://company.okta.com/oauth2/default/.well-known/jwks.json | \ jq -r '.keys[0].x5c[0]' | \ base64 -d | \ openssl x509 -inform DER -pubkey -noout > /tmp/okta-public.pem
echo $TOKEN | \ openssl dgst -sha256 -verify /tmp/okta-public.pem -signature <(echo $TOKEN | cut -d. -f3 | base64 -d)
# 5. Check expirationEXP=$(echo $TOKEN | cut -d. -f2 | base64 -d 2>/dev/null | jq -r .exp)NOW=$(date +%s)if [ $EXP -lt $NOW ]; then echo "TOKEN EXPIRED"else echo "Token valid for $(( ($EXP - $NOW) / 60 )) more minutes"fiAPI Server Authentication Logs
# View authentication attemptskubectl logs -n kube-system kube-apiserver-* | grep -E "authentication|authorization" | tail -100
# Parse structured logskubectl logs -n kube-system kube-apiserver-* --since=1h | \ jq -r 'select(.msg | contains("authentication")) | "\(.ts) \(.user.username) \(.verb) \(.objectRef.resource)/\(.objectRef.name) \(.responseStatus.code)"'
# Track specific userkubectl logs -n kube-system kube-apiserver-* --since=1h | \ jq -r 'select(.user.username == "okta:sarah@company.com")'Security Hardening Checklist
Pre-Production
- Enable MFA for all Okta users
- Configure session timeout (1-4 hours)
- Set token rotation policy
- Implement IP allowlisting
- Enable Okta threat insights
- Configure SIEM integration
RBAC Hardening
- Remove default service account tokens
- Implement least privilege principle
- Regular RBAC audit reviews
- Namespace isolation policies
- Pod security standards enforcement
Network Security
- Private EKS endpoint
- Network policies for all namespaces
- Service mesh with mTLS
- Ingress controller with WAF
- DDoS protection enabled
Monitoring
- Authentication metrics dashboard
- Failed auth alerting
- Audit log forwarding
- Anomaly detection rules
- Regular security assessments
Conclusion
This deep technical implementation of Okta OIDC for AWS EKS provides:
- Complete Security: End-to-end encryption, MFA enforcement, audit logging
- Scalability: Handles thousands of authentications per second
- Reliability: Multi-region failover, token refresh, break-glass access
- Compliance: SOC2, ISO27001, HIPAA ready
- Developer Experience: SSO, automatic provisioning, self-service
The implementation journey requires careful planning but delivers massive operational and security benefits. Start with a proof of concept, validate with a pilot team, then roll out systematically.